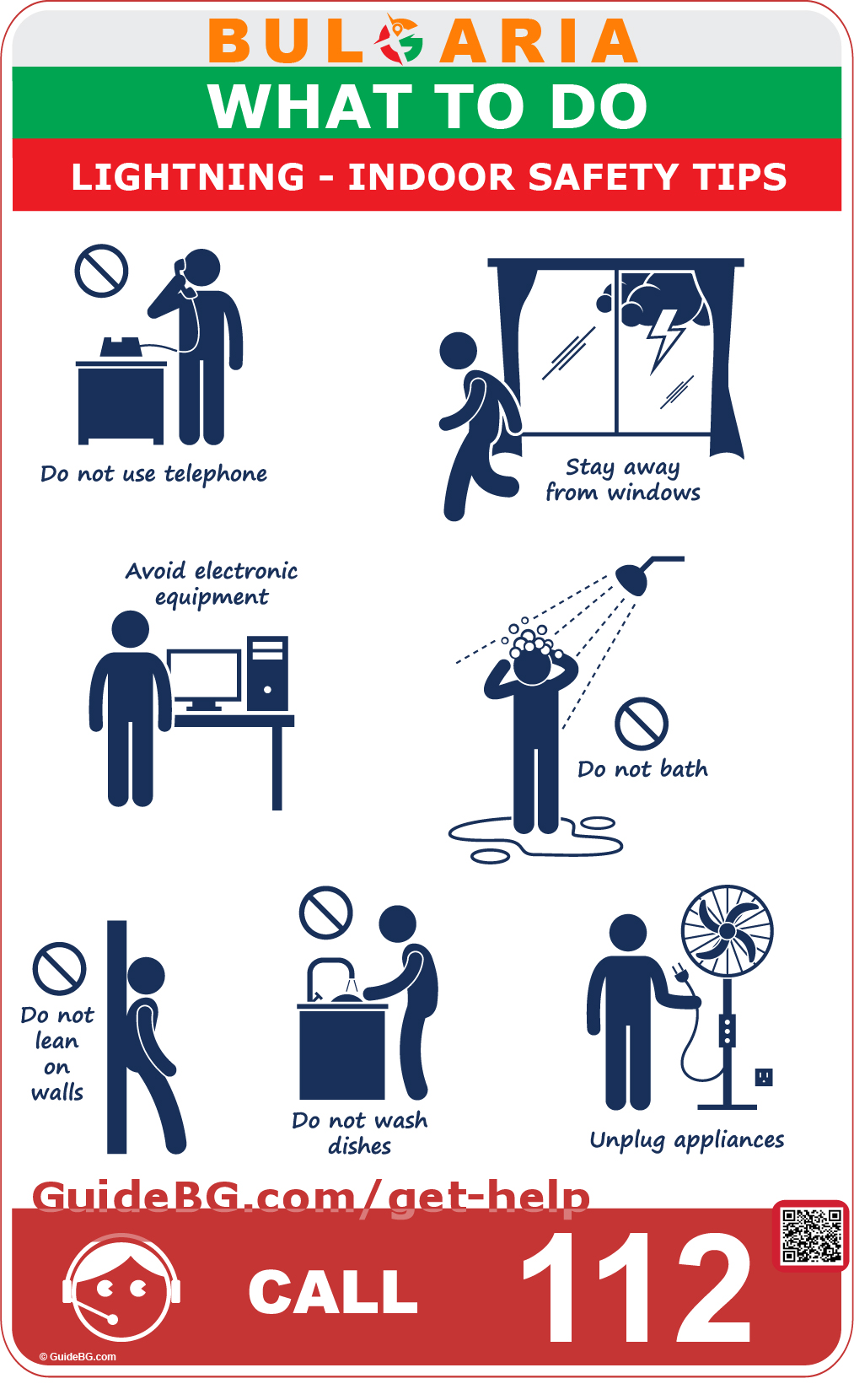
Even within the seeming safety of your home, lightning can pose significant risks. Here’s how to stay safe indoors when lightning strikes:
Land Phones Are a No-Go
Electrical current travels through telephone wires, so avoid using corded phones as they can conduct the electric charge.
Stay Clear of Window
Windows can shatter if struck by lightning or due to strong winds, so it’s safer to stay away from them during a storm.
Electronics and Lightning Don’t Mix
Surge protectors might not be enough to save electronics from a lightning strike’s power, so avoiding using them is best.
Pause the Baths
Water and metal pipes conduct electricity, so avoid bathing to eliminate the risk of a lightning strike reaching you through plumbing.
Door Caution
Like windows, doors can have metal components that conduct electricity, so leaning against them is risky during a storm.
Do Not Lean on Walls
Leaning on doors (or any conductive materials like metal frames) during a lightning storm is generally discouraged due to the risk of electrical conduction.
Hold Off on the Dishes
Metal sinks and faucets are conductive, and since electrical current can travel through pipes, it’s best to avoid washing dishes.
Unplug for Protection
Unplugging appliances can prevent damage from electrical surges caused by lightning.
Research and Theoretical Background
Lightning Conductivity
Lightning is a massive electrical discharge between the atmosphere and an earth-bound object. Many materials, especially metals, can conduct electricity. The electrical current in a lightning strike can exceed 30,000 amperes, and the voltage can range from a few million to over a hundred million volts. The temperature of the lightning channel can reach as high as 30,000°C (54,000°F), which is hotter than the surface of the Sun. If lightning strikes a building or a structure that is conductively connected to something you are touching (like a metal door frame), the electrical current can be conducted through the material and potentially through your body, leading to severe injuries or even fatality.
Lightning Voltage Gradients
Nearby strikes can create voltage gradients across the ground and through buildings, even without direct contact. Being in contact with conductive paths that are part of these gradients can increase the risk of receiving a shock.
Safety Precautions
It’s best to avoid contact with anything that can conduct electricity during a storm. This includes avoiding water, electrical equipment, and phones with cords. Safe shelters are typically fully enclosed buildings with wiring and plumbing that can provide a path for the lightning charge to follow into the ground, reducing the risk to occupants.
Being indoors is your safest bet in a storm, provided you implement crucial measures to minimize the risk of lightning-related injuries. Your home is your refuge, so you must follow specific precautions to protect it and yourself. Additionally, referring to outdoor safety tips can further enhance your preparedness and safety.